Although fitness magazines tout the benefits of diet and exercise, many individuals struggling with obesity cannot lose the weight through lifestyle changes alone. Fortunately, certain medical interventions have been shown to help obese individuals achieve a healthy weight. One of the most frequently performed weight loss surgeries is gastric bypass, which can lead to weight loss and improvement in overall health.
Gastric bypass is the oldest of the bariatric surgeries and as such has the highest number of surgeons trained in performing it as well as the longest history of results. However, more recent surgical techniques may offer similar results with less side effects.
What Does Gastric Bypass Surgery Entail?
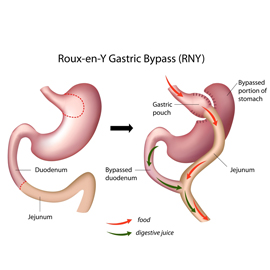
Gastric bypass is a type of procedure within the larger category of bariatric, or weight loss, surgery. During this procedure, the surgeon separates the stomach into a larger and a smaller portion. The physician then connects the smaller stomach pouch to the small intestine.
This surgery has two main effects. First, the stomach no longer holds as much food, allowing obese individuals to feel full after eating smaller portions. Second, the surgery bypasses the first portion of the small intestine, called the duodenum. The duodenum is where many of the calories are absorbed from food. Bypassing this region limits calorie absorption and spurs weight loss. These two effects increase the rate of weight loss by dramatically decreasing caloric intake without the patient feeling hungry all of the time.
What to Know Before You Choose Bypass Surgery
In most cases, bypass surgery is performed laparoscopically. This means that small incisions are made in the belly, allowing the surgeon to insert very small tools through these cuts. As a result, most people who undergo gastric bypass surgery experience minimal scarring and a relatively short recovery time. You may need to stay in the hospital for a few days following the surgery, and a full recovery may take several weeks. However, gastric bypass has the highest rate of complications in the immediate post-surgical period and some and complications such as leaks may be life-threatening.
Many patients who undergo gastric bypass surgery lose 60 percent of their weight or more. However, the surgery is not for everyone. A successful outcome depends on the patient making lifestyle changes. It is important to eat several small meals throughout the day, because the stomach cannot handle large amounts of food at once. Additionally, regular physical activity is necessary to promote weight loss and overall health.
Although Gastric Bypass surgery leads to significant weight loss, it is not without risk and may not be the first choice to consider when weighing bariatric surgery options. Gastric bypass involves a permanent change in gastrointestinal anatomy. The division of the stomach and the creation of new connections in the intestines requires cutting and stapling within the body increasing the chances of internal leaks in the immediate post-operative period. Leaks have the potential of being life threatening and usually require additional surgeries to correct.
Separating the stomach during the gastric bypass reroutes the flow of food in such a way that its passage through the stomach is no longer controlled by a valve at the base of the stomach. Rapid emptying of the stomach especially after eating sugary or high carbohydrate foods results in a condition called Dumping Syndrome. This unpleasant situation is relatively common and while some see it as a deterrent to eating sugary food, others find its symptoms inconvenient and often embarrassing as they mimic an acutely upset stomach with cramping, pain, nausea and vomiting and severe uncontrollable diarrhea.
When considering weight loss surgery, LAP BAND surgery is a less invasive and reversible option with good long term weight loss results that may meet your needs in preference to more invasive procedures such as gastric bypass.