While diet and exercise help many lose weight, others who struggle with obesity and obesity-related illnesses find that they cannot take excess weight off through lifestyle changes alone. Weight loss surgery has been shown to help these patients lose weight and to see relief from obesity-related maladies that include type 2 diabetes, heart disease and arthritis. Gastric sleeve surgery may offer hope to those struggling with weight control.
There are a number of weight loss surgery — also known as bariatric surgery — choices available. However, not every technique is ideal for every weight loss patient.
What’s Involved with Gastric Sleeve Surgery?
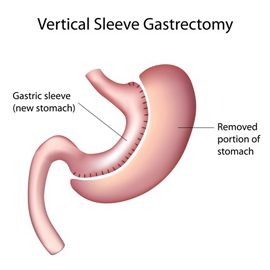
Gastric sleeve surgery is a restrictive surgery that makes your stomach smaller. With a smaller stomach, you are unable to eat as much as and feel full more quickly. In gastric sleeve surgery, more than half of the stomach is removed, leaving behind a slim vertical tube. Because stomach tissue is removed, this is not a reversible surgery.
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia. The surgery can either be performed by making a large abdominal incision or laparoscopically. This surgery is sometimes performed as a step before gastric bypass or duodenal switch surgery.
What You Need to Know Before Choosing Sleeve Gastrectomy Surgery
Recovery and a return to normal activities can take several weeks after surgery. For about the first month after gastric sleeve surgery, patients are restricted to a liquid diet. Soft foods and then small amounts of other foods are gradually added to the patient’s diet. Patients will be able to return to work about 4 to 6 weeks after surgery, and a fuller diet over a period of around three months. Unlike options like gastric band surgery, gastric sleeve surgery is permanent.
As with any surgical procedure, gastric sleeve surgery is not risk-free. Over time, some patients have trouble absorbing adequate amounts of vitamins and minerals because a significant portion of the stomach is removed. Patients will need to work with their doctors over a long period of time to make sure that their nutritional needs are met. Other risks include risk of infection at the incision point, blood clots in the lung and leaks from the stomach into the abdominal cavity.
Patients who opt for gastric sleeve surgery typically lose about half of their excess weight. Those who commit to the necessary lifestyle changes have higher rates of success. Keeping medical appointments, regular exercise and following recommended eating plans are all necessary for permanent weight loss.